In the modern corporate world, stock-based compensation has become a key tool used by companies to attract, retain, and motivate employees, particularly in the tech and startup sectors. This form of compensation involves offering company stock or stock options as part of an employee’s overall pay package. For investors and employees alike, understanding stock-based compensation is essential, as it can have a significant impact on a company’s financials, stock price, and overall performance. In this article, we’ll explore what stock-based compensation is, how it works, and how it affects both employees and investors.
What is Stock-Based Compensation?
Stock-based compensation refers to the practice of paying employees, executives, or directors with stock in the company instead of, or in addition to, traditional cash compensation. There are several forms of stock-based compensation, the most common being:
- Stock Options: Employees are granted the right to purchase company stock at a fixed price (often referred to as the exercise price) for a specified period. If the company’s stock price rises above the exercise price, employees can purchase shares at the lower price and sell them at the current market price, making a profit.
- Restricted Stock Units (RSUs): RSUs are promises to deliver company stock at a future date, provided certain conditions (such as vesting periods) are met. Unlike stock options, RSUs do not require employees to purchase the stock. They are typically granted as part of an employee’s compensation package and become valuable once vested.
- Stock Grants: These are outright gifts of company stock, often provided as bonuses or performance-based awards. Stock grants do not require employees to buy the stock but are subject to conditions like performance targets or tenure.
Why Do Companies Use Stock-Based Compensation?
- Attracting Talent: Especially for startups and high-growth companies that may not have the cash flow to offer large salaries, stock-based compensation provides a way to attract top talent. Employees are incentivized to join the company with the potential for substantial financial gains if the company’s stock performs well.
- Retention and Motivation: Stock-based compensation is often tied to vesting schedules, meaning employees must stay with the company for a certain number of years or meet specific performance goals to fully earn their stock awards. This encourages loyalty and helps retain key talent. Additionally, since the value of stock options or RSUs is linked to the company’s performance, employees are motivated to work hard to increase the company’s stock price.
- Aligning Interests: By offering stock-based compensation, companies align the interests of their employees with those of their shareholders. Employees who hold company stock are more likely to act in the best interest of the company, focusing on long-term growth and profitability, knowing that their personal financial success is tied to the company’s stock performance.
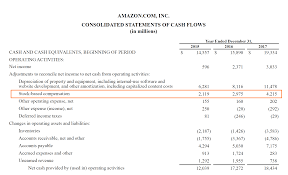
The Impact of Stock-Based Compensation on Investors
While stock-based compensation can benefit employees, it’s important for investors to understand how it may impact a company’s financial health and stock price. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Dilution of Shares
One of the primary concerns for investors is dilution. When a company grants stock options, RSUs, or stock grants, it often issues new shares, which can increase the total number of shares outstanding. This dilutes the ownership percentage of existing shareholders, potentially reducing the value of each share. While stock-based compensation can be a powerful incentive tool, investors should consider whether the potential dilution is justified by the company’s growth and future prospects.
2. Stock-Based Compensation as an Expense
Although stock-based compensation is not a cash expense, it is considered a non-cash expense on the income statement. According to accounting standards, companies must recognize the cost of stock options and RSUs as an expense over the vesting period. While this expense does not directly affect cash flow, it can reduce reported profits. Investors should be mindful of how stock-based compensation affects a company’s earnings and profitability, particularly when comparing companies with different compensation structures.
3. Incentive to Perform
For investors, stock-based compensation can be a sign that a company is effectively incentivizing its employees to drive the company’s success. The idea is that employees will work harder and make decisions that benefit long-term growth because they directly benefit from increases in the stock price. In this way, stock-based compensation can be seen as a positive for shareholders, as it creates alignment between employees and investors.
4. Impact on Valuation
Investors should also consider how stock-based compensation affects a company’s valuation. For example, if a company grants a large number of stock options, the potential dilution from these options may be factored into its valuation, which could impact its price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio or other valuation metrics. Investors should carefully examine a company’s compensation disclosures to understand the potential future impact of stock-based compensation on its stock price.
How to Assess Stock-Based Compensation When Investing
When evaluating companies that use stock-based compensation, investors should look for transparency in how the company reports stock-based compensation expenses. The 10-K or annual report often provides valuable information about the number of stock options or RSUs granted, the vesting schedules, and the potential impact on future dilution.
Investors should also assess whether the use of stock-based compensation is reasonable compared to the company’s growth prospects. If the company is a high-growth startup, stock-based compensation may be a vital tool for attracting talent. However, for established companies, excessive stock-based compensation without clear performance objectives can be a red flag.
Conclusion
Stock-based compensation is an important aspect of modern corporate compensation strategies, benefiting both employees and companies by offering incentives tied to company performance. However, it’s essential for investors to understand how it affects a company’s financials, particularly in terms of potential dilution, expenses, and alignment with long-term growth objectives. By evaluating stock-based compensation practices, investors can make more informed decisions and better assess the long-term value of a company.
If you’re looking to trade or invest in companies that use stock-based compensation, JD Trader provides an easy-to-use platform with tools to track company performance, analyze financial reports, and make informed investment decisions. Understanding how stock-based compensation impacts a company’s stock price can give you a competitive edge in your investment strategy.
This article is optimized for SEO with the keyword “stock-based compensation” and aims to provide valuable insights for investors who want to understand the impact of stock-based compensation on both company performance and stock price.

